How Endoscope Insertion Improves Medical Procedures
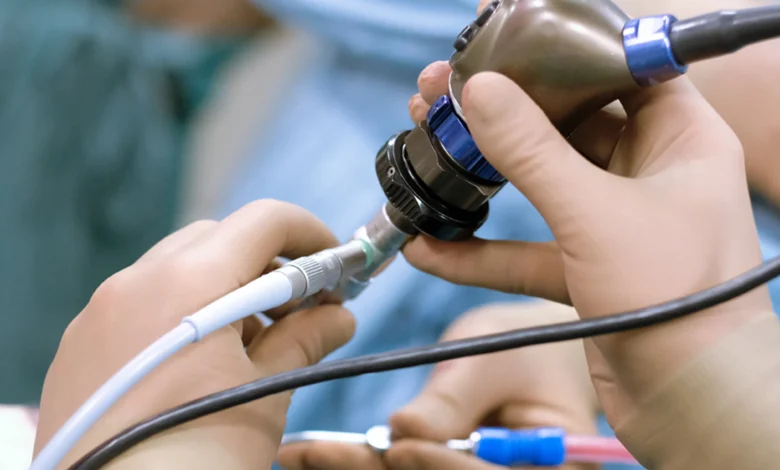
Endoscope insertion has revolutionized the medical world, allowing doctors to perform complex procedures with greater precision and less risk. In simple terms, an endoscope is a long, flexible tube equipped with a light and camera that allows doctors to see inside the body without the need for large incisions. This minimally invasive technique has improved patient care, enabling faster recoveries and more accurate diagnoses. Let’s explore how endoscope insertion improves medical procedures and benefits both patients and healthcare professionals.
How Endoscope Insertion Works in Medical Procedures
Endoscope insertion is a critical process in many medical procedures. By guiding the endoscope through small incisions or natural openings, doctors can examine organs, tissues, and cavities that would be hard to reach otherwise. This method not only improves effectiveness but also minimizes physical trauma compared to traditional surgery, resulting in quicker recovery and fewer complications.
Endoscopes come in various forms for specific procedures, such as gastrointestinal (GI) exams, arthroscopies, and bronchoscopies. This versatility is one reason why endoscope insertion is preferred by many healthcare practitioners.
A stress relief boot is often added to endoscopes to protect the device from excessive bending or wear during insertion. This feature helps maintain the device’s flexibility and durability, ensuring optimal performance over time.
The Role of Endoscope Insertion in Diagnosing Medical Conditions
One of the most significant advantages of endoscope insertion is its ability to assist in the diagnosis of numerous conditions. In the past, many diseases required invasive surgery to diagnose. Now, with endoscopy, doctors can see the internal structures clearly and accurately, reducing the need for invasive procedures. For example, gastrointestinal endoscopes can help identify ulcers, tumors, and areas of inflammation, while bronchoscopes are crucial for diagnosing lung conditions such as cancer or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Moreover, endoscope insertion allows for real-time viewing, providing immediate results during the procedure. This gives doctors a clear understanding of what is happening inside the body and allows them to make decisions on the spot, making diagnoses faster and more reliable.
How Endoscope Insertion Improves Treatment and Surgery
Not only does endoscope insertion aid in diagnosis, but it also plays a crucial role in treatment. For instance, in gastrointestinal procedures, doctors can perform biopsies, remove polyps, or stop internal bleeding through the endoscope, eliminating the need for more invasive surgery. Similarly, during joint surgeries, an arthroscope can be used to repair damaged cartilage or tissue, offering a less painful alternative to traditional surgery.
The minimally invasive nature of endoscope insertion means that patients often experience shorter recovery times, less pain, and fewer complications. The smaller incisions reduce the risk of infection and scarring, which are common concerns in conventional surgeries.
Benefits of Endoscope Insertion for Patient Recovery
Patients undergoing procedures involving endoscope insertion often experience quicker recovery times compared to those who have traditional surgeries. Since endoscopes are inserted through small incisions, patients generally have less post-operative pain and can return to normal activities faster. For example, in laparoscopy, a common type of endoscopic surgery used for abdominal issues, patients may be able to return to work within a few days, compared to the weeks or even months required for recovery from traditional surgery.
Furthermore, the precision of endoscope insertion reduces the amount of tissue trauma, leading to a less invasive procedure overall. This contributes to faster healing times and reduces the likelihood of complications such as infections or excessive bleeding.
Applications of Endoscope Insertion in Various Medical Specialties
Endoscope insertion has found applications in a variety of medical specialties, improving both diagnostic and therapeutic outcomes. Some of the major fields where endoscopes are used include:
- Gastroenterology: In procedures like colonoscopies and upper GI endoscopies, doctors can inspect the digestive tract for issues such as inflammation, cancer, and ulcers.
- Orthopedics: Arthroscopy allows surgeons to examine joints and tissues, as well as perform surgeries to treat conditions like torn ligaments or cartilage damage.
- Pulmonology: Bronchoscopy is used to visualize the lungs and airways, helping to diagnose conditions such as lung cancer, infections, or chronic diseases.
- Urology: Cystoscopy helps examine the bladder and urethra, often used to detect urinary tract issues or cancer.
By enhancing doctors’ ability to diagnose and treat conditions quickly, endoscope insertion has become an essential tool across many specialties.
Safety and Precautions During Endoscope Insertion
Although endoscope insertion is generally considered safe, it’s essential for healthcare providers to take necessary precautions to minimize risks. Before the procedure, patients may be given a sedative or anesthesia to ensure comfort. Furthermore, doctors must carefully assess the patient’s condition and determine the most appropriate type of endoscope to use.
Complications are rare but can include infection, bleeding, or injury to surrounding organs. However, with skilled professionals and modern technology, these risks are minimal. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions before and after the procedure to ensure the best possible outcomes.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of endoscope insertion in medical procedures?
Endoscope insertion is used to view internal body structures for diagnostic and treatment purposes. It allows doctors to examine organs and tissues with minimal invasiveness.
2. Is endoscope insertion painful?
The procedure is typically not painful because sedatives or anesthesia are administered. Afterward, there may be mild discomfort, but it usually subsides quickly.
3. How long does recovery take after an endoscopic procedure?
Recovery times are generally short, often taking only a few days to a week, depending on the procedure. Most patients can return to their daily activities sooner than after traditional surgery.
4. Are there risks associated with endoscope insertion?
While complications are rare, there may be risks such as infection, bleeding, or injury to nearby organs. These risks are minimized with experienced medical professionals and proper aftercare.
5. Can endoscope insertion be used for all types of surgery?
Endoscope insertion is effective for many procedures, but not all surgeries can be performed using this method. It is best suited for diagnostic and minimally invasive treatments.
Conclusion
Endoscope insertion has truly transformed the landscape of modern medicine. It allows for more accurate diagnoses, reduces the risks associated with invasive surgeries, and accelerates recovery times for patients. With its application across multiple specialties, endoscope insertion continues to play a critical role in improving patient outcomes and advancing medical procedures. As technology evolves, we can expect even greater innovations in the field, further enhancing the precision and effectiveness of endoscopic procedures.